Imagine a India where your neighbourhood Kirana store is just as easily accessible online as giant e-commerce platforms. That’s the vision behind ONDC, India’s Open Network for Digital Commerce. It’s not an app or a website, but a set of rules that connect buyers, sellers, and technology companies in a more open and inclusive way.
Think of it as a public highway for e-commerce:
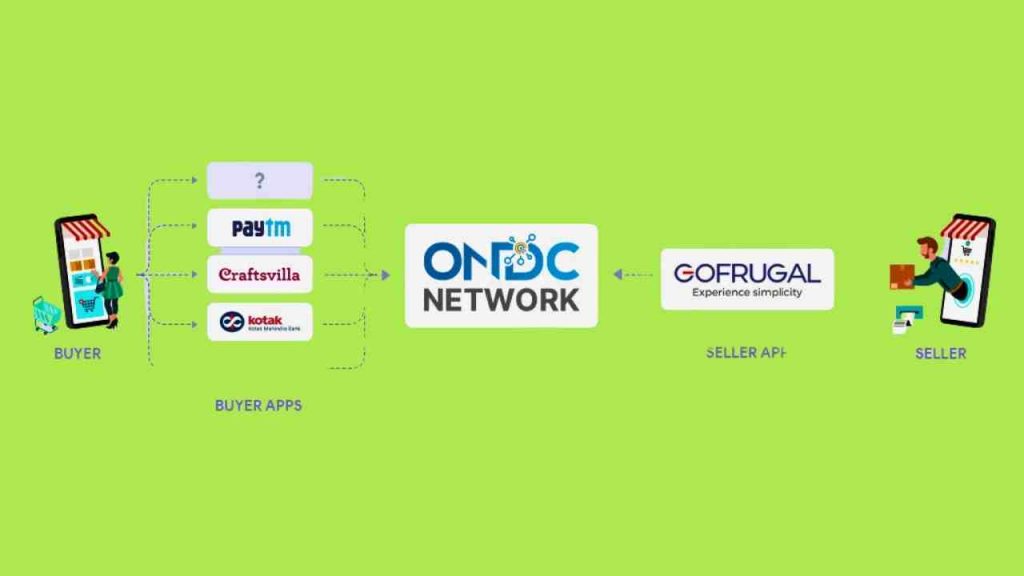
- Sellers: Anyone can join, from big brands to small shops, creating a level playing field.
- Buyers: You can compare prices and products across different platforms, seamlessly, in one place.
- Tech companies: They can build apps and services on top of ONDC, fostering innovation and competition.
The goal?
- Empower small businesses: Give them a chance to compete online, boosting local economies.
- Increase consumer choice: Break the dominance of existing platforms, offering wider options and fairer prices.
- Create a more inclusive digital economy: Bring millions of small businesses and consumers into the fold.
Challenges for ONDC’s success in India:
Adoption and Participation:
- Attracting existing players: Established e-commerce giants with deep customer bases and infrastructure pose a significant challenge. ONDC needs to offer compelling reasons for them to join.
- Onboarding small sellers: Integrating millions of small businesses, especially Kirana stores, requires overcoming technical hurdles and providing easy onboarding processes.
- Consumer awareness and trust: Building trust and awareness among consumers who are already accustomed to existing platforms is crucial.
Operational hurdles:
- Delivery and logistics: ONDC currently lacks a robust and unified delivery network, impacting order fulfillment and customer experience.
- Grievance redressal: A clear and efficient grievance redressal mechanism is essential to build trust and resolve user issues promptly.
- Standardization and interoperability: Ensuring seamless integration across different buyer and seller apps with standardized data formats is crucial for smooth functioning.
Technological challenges:
- Scalability: The platform needs to handle large volumes of transactions and users while maintaining efficiency and reliability.
- Data security and privacy: Concerns regarding data security and privacy need to be addressed to ensure user trust and comply with regulations.
- User interface and experience: Offering a user-friendly and intuitive experience across diverse buyer and seller apps is vital for user adoption.
Policy and regulatory issues:
- Level playing field: Ensuring a fair and competitive environment for all participants, including existing players, is crucial.
- Regulatory clarity: Clear and consistent regulations are needed to address issues like data ownership, consumer protection, and competition.
Scope of success or failure:
While challenges exist, ONDC also has potential for success:
- Government backing: ONDC enjoys government support, providing resources and facilitating adoption.
- Open and democratic model: The open network approach promotes competition and empowers sellers, potentially benefiting consumers.
- Focus on local businesses: ONDC can empower local businesses and Kirana stores, promoting inclusivity and economic growth.
Whether ONDC succeeds or fails depends on its ability to overcome these challenges. Addressing operational hurdles, building trust, and fostering user adoption are crucial. If successful, ONDC could reshape India’s e-commerce landscape, promoting a more open, competitive, and inclusive ecosystem. However, navigating and overcoming the aforementioned challenges will be critical to achieve this vision.
How ONDC can benefit tech startups in India:
1. Level playing field: ONDC removes dependence on established e-commerce platforms, allowing startups to compete directly with larger players. This opens doors for them to showcase their unique offerings and build user bases without facing the limitations of existing platforms’ algorithms and fees.
2. Increased market reach: By connecting directly with buyers on the ONDC network, tech startups can access a wider audience beyond their own apps or websites. This opens up new opportunities for customer acquisition and market expansion.
3. Innovation opportunities: ONDC’s open-source nature allows startups to build innovative solutions and services on top of the network. This could include:
- Developing new buyer and seller apps: Startups can create user-friendly interfaces tailored to specific needs, catering to diverse customer segments.
- Building logistics and fulfillment solutions: Streamlining delivery and logistics for ONDC sellers could become a valuable service for startups.
- Providing data analytics and marketing tools: Helping businesses leverage ONDC data to gain insights, optimize their offerings, and reach target audiences effectively.
4. Collaboration and partnerships: ONDC fosters collaboration between different players in the ecosystem. Startups can partner with established businesses, logistics providers, and other tech startups to offer comprehensive solutions and services to buyers and sellers on the network.
5. Government support: ONDC enjoys backing from the Indian government, potentially leading to initiatives and resources that support the growth of startups participating in the network. This could include funding opportunities, mentorship programs, and access to technical expertise.
While ONDC is a unique initiative with no direct equivalent in other countries, there are various projects and initiatives across the globe sharing certain similarities and exploring similar goals:
Similar Goals:
- Empowering small businesses:
- South Korea: The government provides support programs and digital platforms to help small businesses enter e-commerce.
- Germany: Mittelstand Digital initiative promotes digitalization for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Open and competitive e-commerce ecosystems:
- EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA): Aims to regulate large online platforms and promote fair competition.
- Japan’s E-commerce Platform Openness Act: Requires large platforms to open their data and systems to competitors.
- Consumer choice and transparency:
- China’s Anti-Monopoly Guidelines: Address concerns about dominant e-commerce platforms.
- US Open Data for Competition Initiative: Aims to increase data access and innovation in digital markets.
However, significant differences exist:
- Scope: ONDC aims to encompass the entire e-commerce ecosystem, while most initiatives focus on specific aspects.
- Government involvement: ONDC enjoys direct government support, unlike initiatives driven by private initiatives or competition authorities.
- Level of openness: ONDC is a fully open network, while others might have restrictions or limitations.
Examples of systems with certain similarities:
- China: While not directly comparable due to its centralized nature, platforms like Pinduoduo and JD.com promote competition and offer diverse seller options.
- Germany: The Shopware platform allows merchants to create independent online stores, offering some level of openness.
- Thailand: The “We Love Thai Products” platform connects local businesses with consumers, promoting similar goals but lacking ONDC’s network-wide approach.
Conclusion: It’s a bold vision, but the road ahead is not without challenges.
It’s important to note that the situation is still evolving, and the ultimate success of ONDC remains to be seen. Continued efforts, strategic partnerships, and addressing user needs will be key factors in determining its outcome.ONDC needs to attract big players, simplify onboarding for small businesses, and build trust with consumers. But if successful, it could revolutionize how India shops online, creating a fairer, more competitive, and truly inclusive digital marketplace.It’s important to note that ONDC is still in its early stages, and its ultimate impact and success remain to be seen. Analyzing how existing initiatives have addressed challenges and achieved their goals could provide valuable insights for ONDC’s future development.
Tech Trailblazers
Read more: Beyond the Layoffs: Reshaping the Tech Future with Agility and Ethics| Stepping into Infinity: Disney’s HoloTile Redefines Virtual Movement| Google Flutter: The Future of Enterprise Mobile App Development

