In today’s digital-first workplace, Single Sign-On (SSO) is essential for user convenience and enterprise security. Two leading platforms that dominate the market for identity management and SSO are Microsoft’s Azure Entra ID (FormerlyActive Directory) (AD) and Google Identity. Both offer robust features and benefits, but they also have limitations. This article explores their pros and cons in terms of user satisfaction, feature usability, and economy, with real-world examples to highlight their effectiveness.
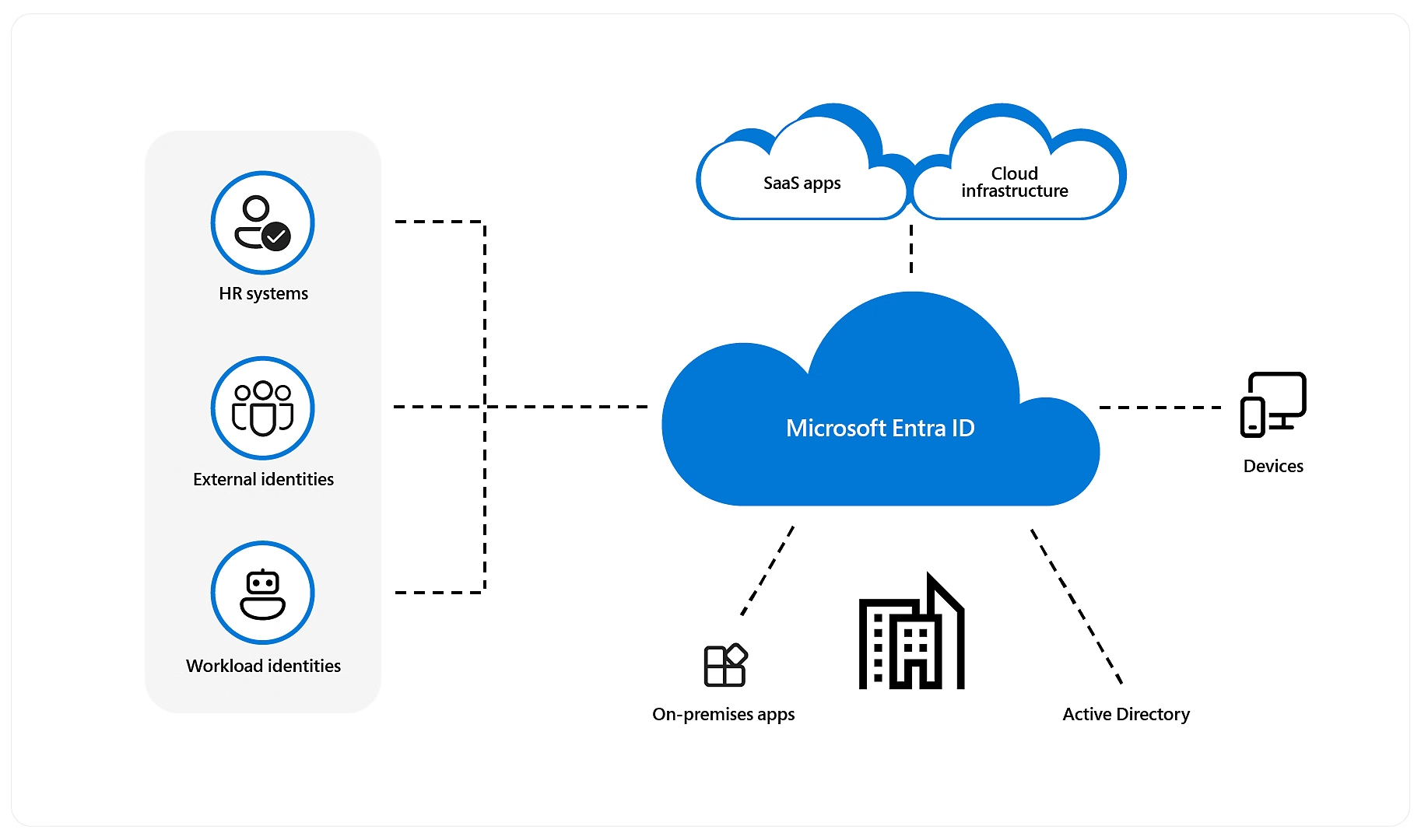
Microsoft Azure Entra ID (FormerlyActive Directory(AD))
Pros
- Deep Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem:
- Azure Entra ID (FormerlyActive Directory) AD is the default identity management system for Microsoft 365, Azure services, and other Microsoft applications.
- Example: Large organizations, like Accenture, that heavily use Microsoft services benefit from seamless integration with Azure AD. Employees use the same credentials across Office 365, Teams, and SharePoint, enhancing productivity.
- Comprehensive Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Azure Entra ID offers advanced RBAC features, enabling organizations to manage complex permission structures efficiently.
- Example: In financial firms, where granular access control is critical for compliance (e.g., Sarbanes-Oxley Act), Azure AD provides the necessary precision to manage user access to sensitive data.
- Conditional Access and MFA:
- Azure Entra ID provides excellent support for Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and conditional access policies.
- Example: A global enterprise like Shell leverages Azure AD’s conditional access to ensure that only users accessing from trusted devices and locations can access sensitive applications, providing an additional layer of security.
- B2B and B2C Support:
- Azure Entra ID supports both Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Consumer (B2C) use cases, making it versatile for organizations.
- Example: A company like Siemens uses Azure Entra ID B2B to manage secure collaboration with external partners while keeping internal systems safe.
- Hybrid Infrastructure Compatibility:
- Azure Entra ID excels in environments where there’s a mix of on-premises Active Directory and cloud-based identity management.
- Example: Volkswagen manages its hybrid infrastructure, using on-prem AD for legacy systems and Azure Entra ID for cloud-native apps, ensuring a unified identity management framework.
Cons
- Complex Configuration for Non-Microsoft Apps:
- While integration with Microsoft apps is smooth, configuring non-Microsoft applications can be cumbersome.
- Example: A company using Salesforce and other third-party tools might require significant customization and time to integrate them with Azure Entra ID.
- Cost:
- Azure Entra ID’s premium features, like conditional access and advanced security monitoring, come with added costs.
- Example: SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) might find the pricing of Azure Entra ID’s higher tiers (P1 and P2) steep compared to Google Identity, especially if their focus is primarily on SSO.
- Learning Curve for Admins:
- Azure Entra ID can be challenging for administrators unfamiliar with Microsoft’s environment. The complexity of Azure’s interface and feature set can slow down adoption.
- Example: IT teams in companies transitioning from traditional directories to Azure AD can face delays in deployment due to the steep learning curve.
Google Identity (SSO)

Pros
- Ease of Use and Deployment:
- Google Identity is renowned for its simplicity and ease of setup, particularly for organizations already using Google Workspace.
- Example: Slack, which integrates with Google Workspace for document sharing and collaboration, can easily tie in Google Identity, streamlining the user experience.
- Cost-Effective:
- Google Identity offers a simpler pricing model, often more affordable for small businesses.
- Example: Startups and small businesses, such as e-commerce firms, can adopt Google Identity at a lower cost without compromising on basic SSO features.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- Google Identity works well with both Google apps and third-party services, offering seamless SSO for web and mobile apps.
- Example: Zapier, a SaaS company, allows its users to integrate Google Identity with various third-party apps, simplifying access and ensuring that users don’t need to remember multiple credentials.
- Excellent for Web-Based Applications:
- Google Identity excels in environments focused on web-based and cloud-native apps.
- Example: Educational institutions, like Harvard University, which use Google Workspace for students and staff, prefer Google Identity for quick deployment and SSO access to learning management systems (LMS).
- Mobile-First Experience:
- Google Identity is highly optimized for mobile users, with seamless integration into Android ecosystems.
- Example: A mobile-first company, such as Uber, might prioritize Google Identity for its ease of use in mobile app environments.
Cons
- Limited Advanced Access Control:
- Google Identity doesn’t offer the same depth in RBAC as Azure AD, limiting control over complex organizational hierarchies.
- Example: A large enterprise like Deloitte might struggle to implement granular access control for internal departments with sensitive data, such as audit and tax services, using Google Identity alone.
- Weaker Hybrid Environment Support:
- Google Identity lacks strong integration with on-premises infrastructure, making it less suited for hybrid IT setups.
- Example: Manufacturing companies that rely on legacy systems and on-premise data centers, like GE, often prefer Azure AD due to its better hybrid infrastructure capabilities.
- Limited Enterprise Features:
- Features like conditional access and real-time monitoring for threats are not as advanced as those offered by Azure AD.
- Example: Banks, such as HSBC, that require high-level security features might prefer Azure AD for its advanced conditional access options.
- Less Comprehensive Third-Party App Integration:
- While Google Identity integrates well with cloud apps, its ecosystem for third-party, enterprise-level apps can be limited.
- Example: Enterprises using ERP solutions like SAP may find that Google Identity doesn’t offer as robust an integration compared to Azure AD.
Comparison at a Glance
| Feature | Azure Entra ID | Google Identity |
|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Moderate, steep learning curve | Simple, easy to deploy |
| Integration with Apps | Excellent for Microsoft apps, moderate for third-party apps | Great for Google apps, decent for third-party apps |
| Advanced Security Features | Advanced (Conditional Access, MFA, RBAC) | Basic MFA, less advanced conditional access |
| Cost | Higher for premium features | More affordable, simpler pricing |
| Hybrid Infrastructure Support | Strong for hybrid (cloud + on-prem) setups | Weaker hybrid support, cloud-first |
| Enterprise Use | Best suited for large organizations with complex needs | Ideal for small businesses, startups, and cloud-native firms |
| Third-Party Integration | Robust for enterprise apps | Limited for enterprise-level integrations |
Which One to Choose?
The choice between Azure Entra ID and Google Identity depends largely on your organization’s needs:
- Choose Azure AD if your organization relies heavily on Microsoft services, has a hybrid infrastructure, or requires advanced security and access controls.
- Choose Google Identity if you want a cost-effective, easy-to-use solution for a cloud-native or Google Workspace-centric organization.
For enterprises with diverse user bases and complex infrastructure, Azure AD offers a more comprehensive solution. However, for startups or companies deeply embedded in the Google ecosystem, Google Identity provides a simpler, more budget-friendly approach.
AI Technology Integration with Access Controls: Exploring the Scope
As organizations increasingly adopt Single Sign-On (SSO) and identity management solutions like Azure Active Directory (AD) and Google Identity, integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into these systems offers transformative opportunities. AI can enhance access control by improving security, user experience, and automation. Let’s explore how AI can be integrated into access controls and some of the most promising use cases for both Azure AD and Google Identity.
1. AI-Enhanced Security
AI can significantly bolster security within access control systems by identifying and preventing unauthorized access and fraudulent activities in real-time. Key capabilities include anomaly detection, adaptive authentication, and predictive security analysis.
Use Cases:
- Behavioral Analytics for User Authentication:
- How it works: AI algorithms monitor user behavior patterns—such as login times, IP addresses, device types, and even typing speed—and flag anomalies that deviate from the user’s typical behavior.
- Example: In a corporate setting using Azure AD, if a user logs in from an unfamiliar location or uses an unusual device, AI can enforce adaptive multi-factor authentication (MFA) or block the login attempt. Google Identity can use a similar AI-driven model to detect suspicious activities across multiple devices.
- Anomaly Detection for Access Control:
- How it works: AI models analyze access logs to detect anomalies, such as abnormal patterns of data access, unusually large file downloads, or repeated access requests from uncommon geolocations.
- Example: Financial institutions like JP Morgan Chase can integrate AI-powered anomaly detection with Azure AD, flagging unusual attempts to access sensitive financial data by insider threats or compromised accounts.
- Predictive Risk Management:
- How it works: AI can use predictive models to identify potential security risks before they happen by analyzing large datasets, including previous security breaches, to detect vulnerabilities in access control systems.
- Example: Healthcare organizations could use AI within Google Identity to predict risks by analyzing patterns in login attempts or access requests to patient records, reducing the risk of data breaches.
2. AI-Driven Adaptive Access Controls
AI can help make access controls dynamic and context-aware. By leveraging AI models, organizations can implement adaptive access controls that change permissions or authentication requirements based on user behavior, risk factors, or organizational context.
Use Cases:
- Contextual Access Control:
- How it works: AI-based systems assess the context (e.g., location, time, device) in which an access request is made and dynamically adjust the level of access or the need for additional authentication steps.
- Example: In Azure AD, a sales executive traveling abroad may require extra authentication for accessing sensitive data outside their usual geolocation. AI can recognize this change and modify access conditions dynamically.
- Role-Based Access Optimization:
- How it works: AI can help automate the creation and updating of role-based access controls (RBAC) by analyzing historical access patterns and suggesting role updates to ensure that users have the appropriate permissions.
- Example: In a multinational corporation, using Google Identity, AI could suggest adjusting roles for employees as they switch between departments or projects, based on their actual access needs. It ensures efficient access control without over-provisioning permissions, reducing the risk of accidental data exposure.
3. Intelligent Automation and User Management
AI can automate and streamline the process of managing users, permissions, and access requests. This reduces the burden on IT administrators, improves the user experience, and ensures timely provisioning and de-provisioning of access.
Use Cases:
- Automated User Provisioning and De-provisioning:
- How it works: AI can automate the onboarding and offboarding process by learning from past user access needs and adapting to organizational changes. It ensures that new users are automatically assigned the correct permissions and that deactivated users lose access without delay.
- Example: For a company using Google Identity, AI could automatically grant a new hire access to relevant apps based on the role and department, ensuring no delays in productivity. In Azure AD, when an employee leaves the organization, AI can revoke all access based on patterns and policies set by the administrator.
- Predictive Role Assignment:
- How it works: AI analyzes user behavior and job function to recommend roles and permissions before they are manually assigned. AI can identify users in similar roles or departments and suggest optimized access policies.
- Example: A company like Coca-Cola, which uses Azure AD, could use AI to suggest the correct permissions for a new marketing employee based on access trends observed in similar roles across the organization.
- AI-Powered Access Request Approval:
- How it works: AI can help automate access approval workflows by analyzing the nature of requests, the user’s role, and access patterns to make recommendations on whether access should be approved, denied, or require additional review.
- Example: In Google Identity, a system administrator could automate access approval for developers requiring access to specific datasets, with AI flagging only high-risk or unusual access requests for manual review.
4. AI-Powered Passwordless Authentication
AI has the potential to drive the adoption of passwordless authentication by using biometrics, device-based authentication, and behavior analytics to replace traditional passwords.
Use Cases:
- Biometric Authentication:
- How it works: AI can enhance biometric systems like facial recognition, voice recognition, or fingerprint authentication, ensuring that only authorized users can gain access based on their physical attributes.
- Example: In a retail chain using Google Identity, AI-powered facial recognition could replace passwords entirely for store employees logging into their systems, streamlining operations and improving security.
- Behavioral Biometrics:
- How it works: AI algorithms track how users interact with devices (e.g., typing speed, touch screen patterns) to continuously authenticate the user based on behavior.
- Example: A law firm using Azure Entra Id could use AI-driven behavioral biometrics to grant or revoke access dynamically based on how an employee interacts with their computer, reducing the need for traditional authentication methods.
5. AI-Powered Incident Response and Remediation
AI can play a pivotal role in automated incident response by detecting security breaches or unusual activities and executing predefined responses to mitigate risks.
Use Cases:
- Automated Threat Detection and Mitigation:
- How it works: AI algorithms can continuously monitor access logs and data transfers to detect unusual patterns that could indicate a security breach. Upon detection, AI can automatically take steps to isolate affected accounts, lock compromised systems, or alert administrators.
- Example: In Azure Entra ID, if AI detects an anomalous login attempt from a suspicious IP address, it can automatically enforce conditional access or suspend the account until the threat is resolved.
- AI-Assisted Compliance Reporting:
- How it works: AI can help organizations maintain compliance by automatically generating reports on access control activities and flagging any compliance risks.
- Example: A healthcare provider using Google Identity could use AI to generate HIPAA-compliant reports on access to patient records, ensuring that any unauthorized access attempts are flagged for review.
Challenges and Considerations
While the integration of AI into access controls offers many benefits, organizations should also be aware of potential challenges:
- Data Privacy: AI systems analyzing access logs and user behavior must comply with data privacy laws such as GDPR. Organizations must ensure that AI-driven insights don’t infringe on user privacy.
- Bias and Accuracy: AI models may carry inherent biases or inaccuracies in detecting anomalies, leading to false positives or negatives. Continuous monitoring and fine-tuning are essential.
- Integration Complexity: AI-enhanced systems may require complex integration into existing identity management platforms, making it essential to choose scalable solutions that can grow with the organization.
Conclusion: The Dominance of Microsoft and Google in Web Authentication and Access Control
As the digital landscape continues to expand, Microsoft and Google remain dominant forces in the realm of web-based authentication and access control. Azure Entra ID and Google Identity have become the cornerstones for millions of enterprises globally, shaping the way organizations secure their applications, manage user identities, and authenticate access across diverse systems.
With the rapid adoption of AI and other emerging technologies, both companies are evolving at a fast pace. Microsoft’s Azure Entra ID leads the way in offering advanced security features, robust integration with on-premises systems, and granular access control, making it a preferred solution for enterprises with complex infrastructures. Google Identity, on the other hand, excels in delivering ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and seamless integration with cloud-native applications, positioning itself as an ideal choice for startups, educational institutions, and cloud-first organizations.
Both platforms are embracing AI to enhance security, improve user experience, and automate access management—whether it’s through adaptive authentication, AI-driven anomaly detection, or passwordless authentication. As these two tech giants continue to integrate AI and other emerging technologies into their access control systems, they will further revolutionize how organizations secure their digital assets.
In the battle for dominance, it’s clear that Microsoft and Google are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, offering businesses the tools they need to stay ahead in an increasingly complex, security-conscious world. The future of web authentication and access control will undoubtedly be shaped by these two leaders, and their innovations will continue to set the standard for the next generation of digital identity management.
Readmore: The AI Revolution: ChatGPT, Microsoft CoPilot, Google Gemini AI, and Meta LLaMA – What’s in It for the Common Man? | Google Gemini: The Superhero of the AI World | Cloud Clash: AWS vs. Azure — Which One Suits You? | Reality vs. Enhancement: Google’s AI-Powered Photo Tools Raise Ethical Questions

